Roughly 68% of the population has an IQ between 85 and 115. But what does that mean? While it’s commonplace for people to reference someone being “high IQ” or “low IQ” in a casual conversation, few people have taken the time to truly understand what an IQ score is or how and IQ test works.
What does IQ mean?
IQ stands for intelligence quotient, and the very concept of an Intelligence Quotient and IQ ratings is controversial. However, it remains a popular tool for job placement and educational services, particularly in regard to helping place children in an appropriate setting for their educational needs. That was really the goal with which Binet was tasked, so it seems fitting that this is the essence of his legacy.
What is an IQ score?
An IQ score is a numerical representation of an individual’s intelligence within a normalized scale of test results. Most modern tests are adjusted so that the mean score is 100, including the most popular Wechsler Intelligence tests. Some IQ tests, like the Cattell Culture Fair test provide a range rather than a specific score to account for measurement error or test bias. You can learn more about popular IQ tests using the links below.
- Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
- Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children
- Woodcock–Johnson Tests of Cognitive Abilities
- Raven’s Progressive Matrices
- Stanford–Binet Intelligence Scale
- Das–Naglieri Cognitive Assessment System
- Cattell Culture Fair III
- Reynolds Intellectual Assessment Scales
- Thurstone’s Primary Mental Abilities
- Kaufman Brief Intelligence Test
- Differential Ability Scales
- Multidimensional Aptitude Battery II
What does IQ measure?
This is a more profound question than it may seem on the surface. Most people would simply answer, “Intelligence.” But what is intelligence? Many people confuse intelligence with knowledge, which is the ability to demonstrate what one has learned. Intelligence instead is defined by Oxford as the ability to acquire and apply knowledge and skills. Where the difficulty comes in is trying to develop a test that can consistently measure an individual’s ability to acquire and apply knowledge independent of factors that would bias the test towards or against people of various cultures, educational opportunities, or personality traits.
For example, attempting to test a child from the United States on “common knowledge” might be more challenging for a child who was born in another country and only recently moved to the United States. Over time, more tests have evolved to try to accommodate for these differences and further break down the components of intelligence. Modern tests look to account for measuring a person’s past learning, visual-spatial and auditory processing, processing speed, short term memory, and abstract reasoning.
What is the IQ scale?
IQ tests are designed to conform to a Bell Curve distribution. This means if you graph them, they make a nice shape that is high in the middle and tapering on both ends that looks a bit like a bell as you can see in the visual distribution of the IQ scale below for the Wechsler Intelligence Scale distribution.
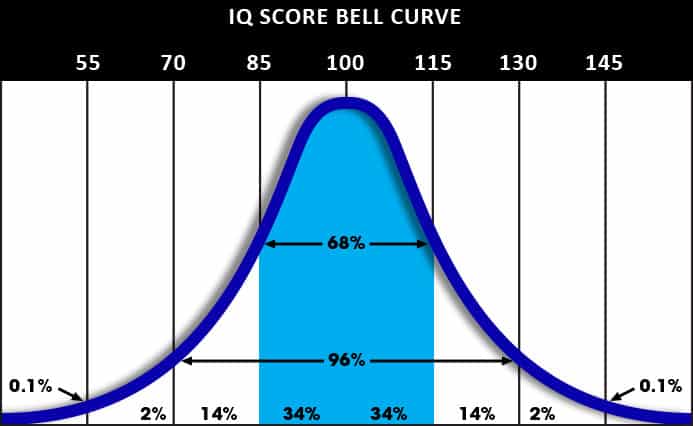
IQ Standard Deviation
As you can see, a Bell Curve is designed so that the majority of the scores lie in the middle of the graph, and as scores get progressively higher or lower the curve slopes down as there are fewer and fewer data points. This distribution is designed to have the average, or mean IQ, right in the middle of the curve. In this case that score is 100. The vertical lines in this chart represent the IQ standard deviation, which is 15 for IQ scores (according to the Wechsler Intelligence Scale). This is a measure of the variability of the data set. A lower standard deviation means that most of the data is very close to the average. A higher standard deviation means there is a greater spread in the results.
The light blue shaded portion of the graph represents one standard deviation above and below the average IQ. As you can see, roughly 68% of people fall in this range of IQs between 85 and 115. Moving out one more standard deviation (IQs between 70-130) will account for more than 96% of the population.
What is an average IQ?
Technically, the average IQ is 100 based on the most popular standard tests like the Wechsler and Stanford-Binet tests. By and large, IQ tests are designed and updated over time to maintain an average of 100. As the bell curve above demonstrated, 68 percent of all IQ scores fall between 85 and 115 points. So, in essence a “normal IQ level” could be said to fall between that IQ range. However, academics have tried taking a more sophisticated approach to categorizing what a normal IQ score is, as well as higher and lower levels of intelligence.
What is considered a high IQ?
A high IQ is a fairly subjective idea. If your criteria is admittance into one of the many high IQ societies, you’ll likely need a score in the 98th percentile or higher. This is the bar set by the most popular high IQ society, Mensa, which requires a 98th percentile or higher score which is a minimum score of 132 on the Stanford-Binet test (which has a slightly different IQ scoring range with a standard deviation of 16).
Of course, these societies set a high bar, and they a very subjective way to view an IQ score.
Many professionals have aimed to classify the various levels of IQ since its inception. One of the first was Lewis Terman, who developed the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales. His initial scale in 1916 classified average intelligence as an IQ between 90-110 with superior intelligence beginning at any score over 110.
Terman IQ Scale (1916)
| IQ Range | Classification |
|---|---|
| Above 140 | "Near" genius or genius |
| 120–140 | Very superior intelligence |
| 110–120 | Superior intelligence |
| 90–110 | Normal, or average, intelligence |
| 80–90 | Dullness, rarely classifiable as feeble-mindedness |
| 70–80 | Border-line deficiency, sometimes classifiable as dullness, often as feeble-mindedness |
| Below 70 | Definite feeble-mindedness |
There were many revisions to this scale over the years, and variations increased as the number of IQ tests grew. Currently, the two most popular IQ tests are the Stanford-Binet and the Wechsler Intelligence Scales, which come in a number of incarnations built for different age ranges.
The most recent IQ classifications for these tests look remarkably similar.
Stanford-Binet IQ Scale (1986)
| IQ Range ("deviation IQ") | Classification |
|---|---|
| 132 and above | Very superior |
| 121–131 | Superior |
| 111–120 | High average |
| 89–110 | Average |
| 79–88 | Low average |
| 68–78 | Slow learner |
| 67 or below | Mentally retarded |
Wechsler IQ Scale
| IQ Range | Classification |
|---|---|
| 130 and above | Very superior |
| 120–129 | Superior |
| 110–119 | High average |
| 90–109 | Average |
| 80–89 | Low average |
| 70–79 | Borderline |
| 69 and below | Extremely low |
So, while there isn’t an exact target for what is considered a “high IQ”, generally speaking, an IQ between 115 and 130 is considered “normal gifted” or “moderately gifted.” Typically, children at this level are put into enrichment programs or classes for gifted children when identified during their school years. People further up the IQ level chart, 130 to 144 are very gifted and typically require more accommodation than your run of the mill enrichment program. They are more likely to be grade skipped, attend college early and so forth.
For more detailed information about specific IQ scores, refer to the following pages:
What IQ is considered genius?
Although some sources say that genius-level IQ starts around 140 or 145, the reality is that the IQ test range most exams can reliably measure to is only 140 or 145. It takes a special assessment by qualified professionals to test the higher reaches of the genius IQ range.
For evidence of this, you don’t need to look any further than Richard Feynman. He is widely considered to be one of the geniuses of his era, yet he took some glee in reporting that his high school IQ test score was merely 125. He declined to join Mensa on the excuse that his IQ wasn’t high enough.
Meanwhile, he won the Putnam by a wide margin. The Putnam is a rigorous math competition that awards scholarships. It has been suggested that his high school IQ test must have been a strongly verbal test that gave short shrift to mathematics.
It gets even more complicated if you have a child who is bright but has special needs or a learning disability. These children are often called “twice-exceptional,” which is sometimes abbreviated 2xE. Their strengths can mask their weaknesses while their weaknesses hide their strengths. Without special testing, they may appear to be average in terms of school performance while being simultaneously bored and frustrated.
For people who have been very frustrated, testing can be useful for identifying exactly what is going on. Having their strengths and weaknesses mapped out can be very refreshing and empowering. This may be the strongest argument for continuing to have and use IQ tests, regardless of their many shortcomings and the controversy that swirls around them.
If you get a score that you feel is too low and you feel doesn’t really represent your ability, it might be best to assume you need more testing. In some sense, that worked for Richard Feynman and he went on to have a wildly successful career.
How do IQ scores differ around the world?
There have been attempts to understand and measure IQs from around the globe, including multiple studies by the controversial English psychologist Richard Lynn. His work in 2010 resulted in a ranked result for 108 countries that some people had structural issues in terms of sample size and targeting of specific segments of their populations. The results did receive some notoriety, however, with the top scoring nations being led by Hong Kong with an average IQ of 108.
| Country | Average IQ |
|---|---|
| Hong Kong | 108 |
| Singapore | 108 |
| South Korea | 106 |
| China | 105 |
| Japan | 105 |
| Taiwan | 101 |
| Iceland | 101 |
| Macau | 101 |
| Switzerland | 100 |
| Austria | 100 |
| Liechtenstein | 100 |
| Luxembourg | 100 |
| Netherlands | 100 |
| Norway | 100 |
| United Kingdom | 100 |
On the other end of the spectrum, the five countries from that study that had the lowest scores included Nigeria, Swaziland, Lesotho, Mozambique, and Malawi.
What is the average IQ in America (United States)?
The average IQ in the United States, according to the work of Richard Lynn in 2009 was 98, just under the global. average of 100 and tied for 24th in his rankings of IQ scores by country. The United States was tied with Australia, Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Latvia, and Spain.
What is the average IQ score in Canada?
According to Lynn’s study, Canada came in one point under the global average of 100 for an average IQ score of 99, one point ahead of the United States.
Does the IQ scale range change over time?
While you might assume that IQ scores are fairly steady, they have in fact shown a consistent increase in IQ in most parts of the world since first being recorded in the early 1900s. This phenomenon was first noticed by James Flynn while comparing military IQ test scores from the 1950s to those in the 1980s. This has since become known as the Flynn Effect. Ultimately, it was discovered that IQ scores had been growing on average about three points per decade. The increase is believed to come from improvements in logical thinking, problem-solving, formal education, and improved nutrition.
Are there IQ differences between races?
For better or worse this continues to be a popular topic both in and outside of psychological circles. That said, multiple studies have shown no genetic correlations between IQ scores for various races. This is also the position of the American Psychological Association.
Are there IQ differences between genders?
Just as with the IQ scores between races, there’s been no evidence to suggest there are differences in average IQ scores between men and women.
Who invented the IQ test?
Alfred Binet, a French psychologist, is credited with being the inventor of the first modern IQ test. Later American tests posited that intelligence was fixed and unbending. This did not agree with his conceptualization of intelligence.
